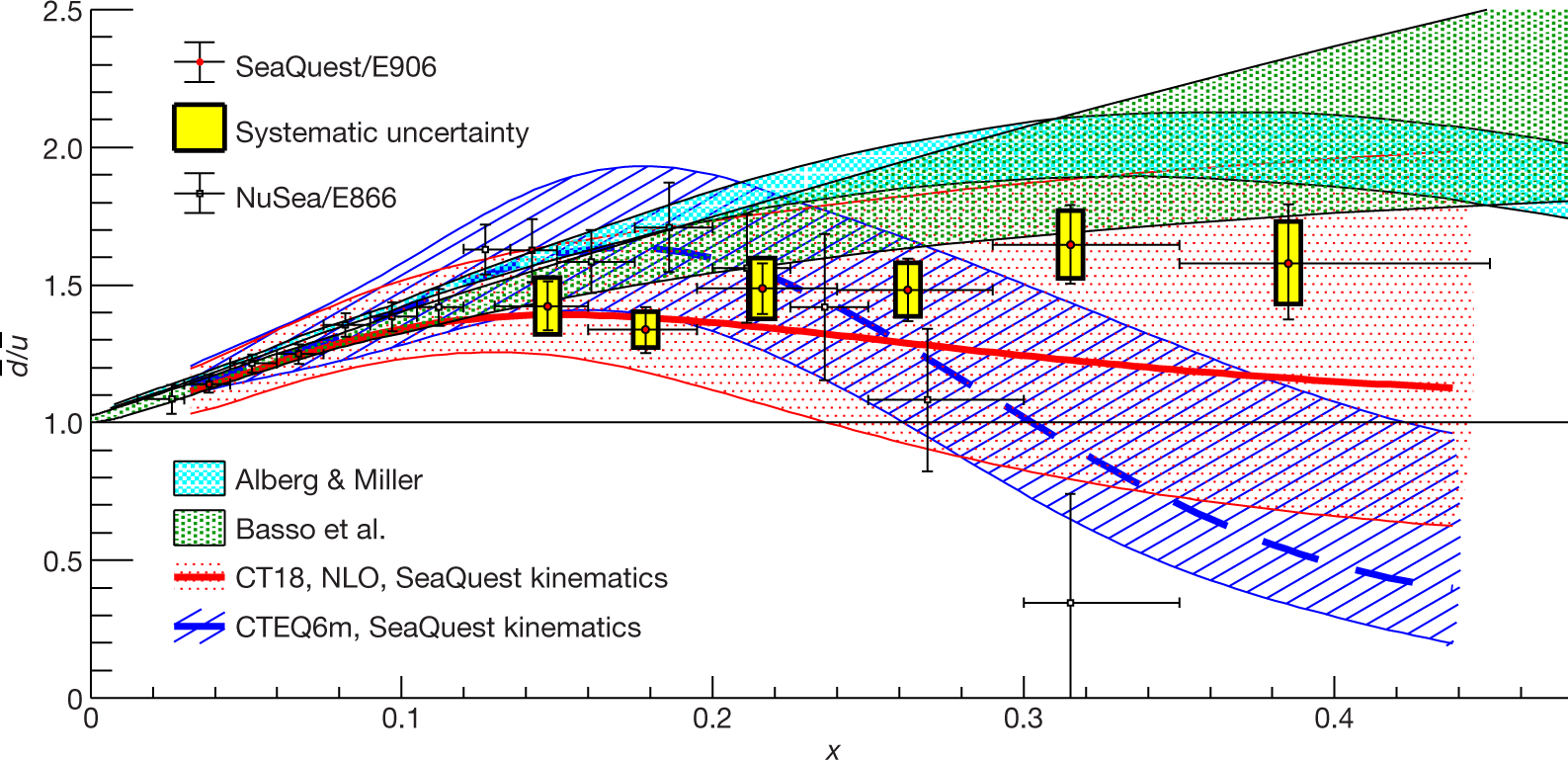
The SeaQuest/E906 Collaboration at Fermilab has published new data on measurements of the ratio of anti-down over anti-up quarks in the proton, obtained by studying the Drell-Yan process in collisions of a 120 GeV proton beam from the Fermilab main injector with protons and neutrons in liquid hydrogen and deuterium targets.
In the Drell-Yan process, quark-antiquark annihilation events are clearly identified by detecting high-energy muon-antimuon pairs resulting from the annihilation of a quark (antiquark) in the beam proton with an antiquark (quark) in the target proton or neutron.
By studying Drell-Yan events in kinematics dominated by beam quarks and target antiquarks with large momentum, and comparing measurements on hydrogen and deuterium under the assumption of charge symmetry (same number of down/anti-down quarks in the neutron as up/anti-up quarks in the proton), the collaboration was able to establish an excess of anti-down quarks over anti-up quarks in the proton. This important and highly anticipated result has no clearly agreed-upon theoretical explanation, and contradicts naive expectations of quark “flavor” symmetry in the antiquark distributions.
The paper can be read here.